

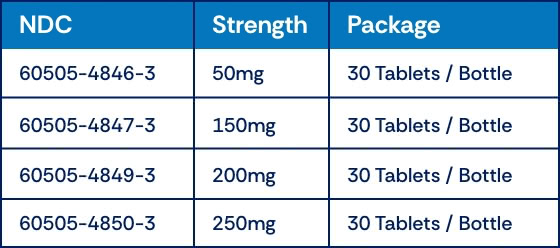
NUVIGIL® (armodafinil) Tablets 50 mg | 150 mg | 200 mg | 250 mg
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
NUVIGIL is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to modafinil or armodafinil.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of NUVIGIL for each indication is as follows:
- Narcolepsy or OSA: 150 mg to 250 mg once a day in the morning.
- SWD: 150 mg once a day, taken approximately one hour prior to start of the work shift.
- Hepatic Impairment: reduced dose in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
- Geriatric Patients: consider lower dose.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious Rash, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: discontinue NUVIGIL at the first sign of rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related.
- DRESS/Multi-organ Hypersensitivity Reactions: if suspected, discontinue NUVIGIL.
- Angioedema and Anaphylaxis Reactions: if suspected, discontinue NUVIGIL.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
NUVIGIL is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to modafinil or armodafinil.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of NUVIGIL for each indication is as follows:
- Narcolepsy or OSA: 150 mg to 250 mg once a day in the morning.
- SWD: 150 mg once a day, taken approximately one hour prior to start of the work shift.
- Hepatic Impairment: reduced dose in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
- Geriatric Patients: consider lower dose.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious Rash, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: discontinue NUVIGIL at the first sign of rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related.
- DRESS/Multi-organ Hypersensitivity Reactions: if suspected, discontinue NUVIGIL.
- Angioedema and Anaphylaxis Reactions: if suspected, discontinue NUVIGIL.
- Persistent Sleepiness: assess patients frequently for degree of sleepiness and, if appropriate, advise patients to avoid driving or engaging in any other potentially dangerous activity.
- Psychiatric Symptoms: use particular caution in treating patients with a history of psychosis, depression, or mania. Consider discontinuing NUVIGIL if psychiatric symptoms develop.
- Known Cardiovascular Disease: consider increased monitoring.
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, NUVIGIL may cause fetal harm. There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to NUVIGIL during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register pregnant patients, or pregnant women may enroll themselves in the registry by calling 1-866-404-4106.
- Ability to Operate Machinery: Although NUVIGIL has not been shown to produce functional impairment, patients should be cautioned about operating an automobile or other hazardous machinery while using NUVIGIL until it is reasonably certain that NUVIGIL therapy will not adversely affect their ability to engage in such activities.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Abuse
- Abuse of NUVIGIL has been reported in patients treated with NUVIGIL. Patterns of abuse have included euphoric mood and use of increasingly large doses or recurrent use of NUVIGIL for a desired effect. Drug diversion has also been noted. During the postmarketing period, misuse of NUVIGIL has been observed (e.g., taking NUVIGIL against a physician's advice, and obtaining NUVIGIL from multiple physicians).
- Abuse of armodafinil, the active ingredient of NUVIGIL, poses a risk of overdosage similar to that seen for modafinil, which may lead to tachycardia, insomnia, agitation, dizziness, anxiety, nausea, headache, dystonia, tremor, chest pain, hypertension, seizures, delirium, or hallucinations. Other signs and symptoms of CNS stimulant abuse include tachypnea, sweating, dilated pupils, hyperactivity, restlessness, decreased appetite, loss of coordination, flushed skin, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- In humans, modafinil produces psychoactive and euphoric effects, alterations in mood, perception, thinking and feelings, typical of other CNS stimulants. In in vitro binding studies, modafinil binds to the dopamine reuptake site and causes an increase in extracellular dopamine, but no increase in dopamine release.
- Modafinil is reinforcing, as evidenced by its self-administration in monkeys previously trained to self-administer cocaine. In some studies, modafinil was also partially discriminated as stimulant-like.
- Physicians should follow patients closely, especially those with a history of drug and/or stimulant (e.g., methylphenidate, amphetamine, or cocaine) abuse. Patients should be observed for signs of misuse or abuse (e.g., incrementation of doses or drug-seeking behavior).
- The abuse potential of modafinil (200, 400, and 800 mg) was assessed relative to methylphenidate (45 and 90 mg) in an inpatient study in individuals experienced with drugs of abuse. Results from this clinical study demonstrated that modafinil produced psychoactive and euphoric effects and feelings consistent with other scheduled CNS stimulants (methylphenidate).
Dependence
- Physical dependence is a state that develops as a result of physiological adaptation in response to repeated drug use, manifested by withdrawal signs and symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug.
- Physical dependence can occur in patients treated with NUVIGIL. Abrupt cessation or dose reduction following chronic use can result in withdrawal symptoms, including shaking, sweating, chills, nausea, vomiting, confusion, aggression, and atrial fibrillation.
- Drug withdrawal convulsions, suicidality, fatigue, insomnia, aches, depression and headache have also been observed during the postmarketing period. Also, abrupt withdrawal has caused deterioration of psychiatric symptoms such as depression.
- Tolerance is a physiological state characterized by a reduced response to a drug after repeated administration (i.e., a higher dose of a drug is required to produce the same effect that was once obtained at a lower dose).
- Multiple cases of development of tolerance to NUVIGIL have been reported during the post marketing period.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Steroidal contraceptives (e.g., ethinyl estradiol):use alternative or concomitant methods of contraception while taking NUVIGIL and for one month after discontinuation of NUVIGIL treatment.
- Cyclosporine: blood concentrations of cyclosporine may be reduced.
- CYP2C19 substrates, such as omeprazole, phenytoin, and diazepam: exposure of these medications may be increased.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of patients were headache, nausea, dizziness, and insomnia.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Apotex Corp. at 1-800-706-5575 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Click here for the full prescribing information.